Urinary Disorders
Most people will have some kind of urinary problem or injury in their lifetime. The common urinary problems include Urinary tract infection, Urinary incontinence, kidney stones, stress incontinence.
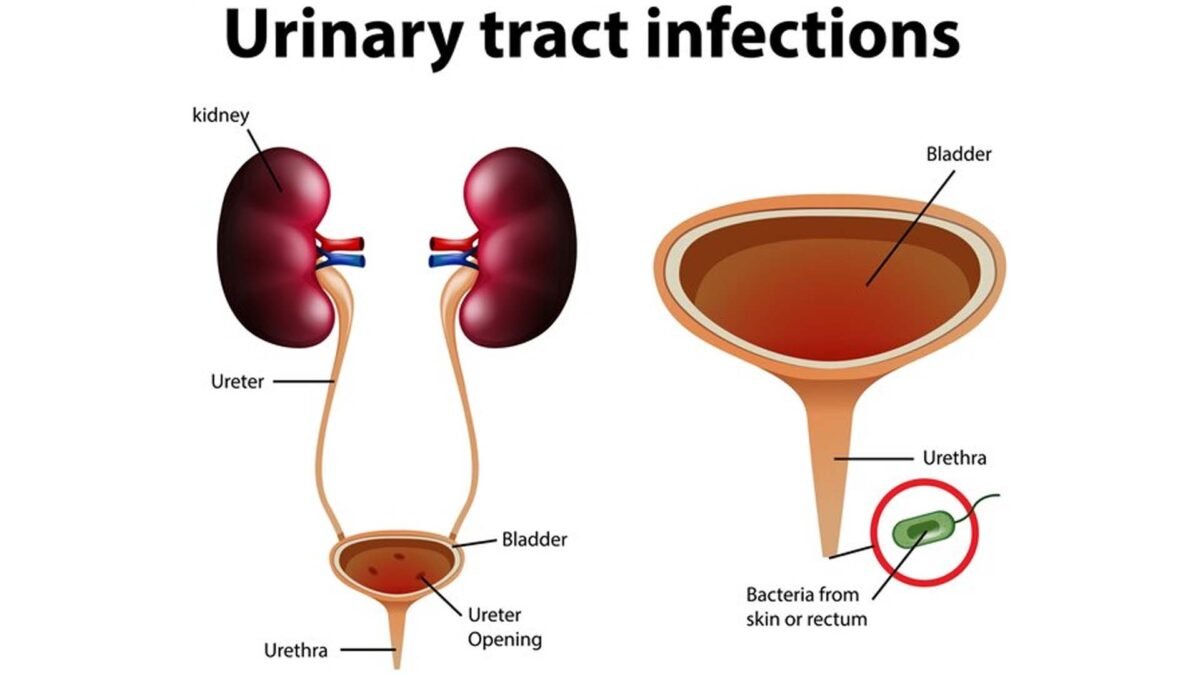
Urinary tract infection is more common among women who are sexually active. Most of the time, UTI bacteria came from the rectal organisms.
Measures to decrease UTI include cleaning the private parts from front to back ( ie. wipe from vagina towards the anus) and to pee and wash the vulval area before and after sex. We also advise patients to drink more water for a few days after sex.
Symptoms:
Common symptoms of urinary problem include:
- Burning sensation when urinating
- Frequent urge to urinate without passing much urine
- Feeling like you cannot completely empty your bladder
- Blood in urine Cloudy, bad smelling urine
Frequent urination, urinary urgency, and urge incontinence – know the difference
Frequent urination is the need to pass urine for more than seven times during the day or less than every two hours.
Urgency is a strong and sudden desire to void which, if not relieved immediately, may lead to urge incontinence.
Urge incontinence is an involuntary leakage of urine, usually preceded by urgency.
What is urinary incontinence?
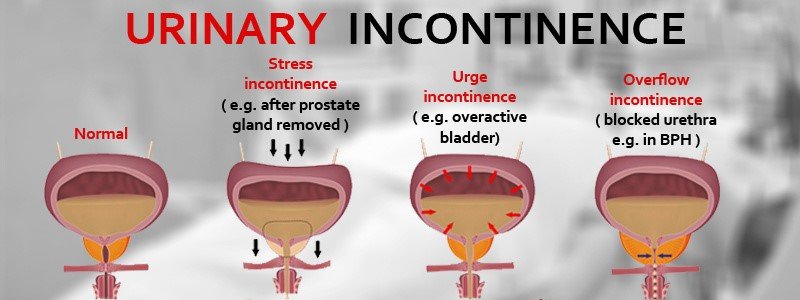
Urinary incontinence refers to an involuntary loss of urine. Types of incontinence include:
- Stress urinary incontinence – involuntary loss of urine associated with coughing, sneezing, carrying heavy things and even running or jumping.
- Urge incontinence – involuntary loss of urine preceded by a sudden strong desire to pass urine and voiding before the ability to reach the toilet.
- Overflow incontinence – involuntary loss of urine due to an inability to empty the bladder well.
What should you do if you have urinary incontinence?
Mild urinary incontinence may not be troublesome but moderate to severe urinary incontinence can have a drastic effect of a women’s quality of life. It can also cause social and hygiene problems.
Management of urinary incontinence
In mild cases regular pelvic floor exercises or some medications can help to improve the incontinence. In severe cases of stress urinary incontinence, surgical correction by your gynaecologist should be considered.





